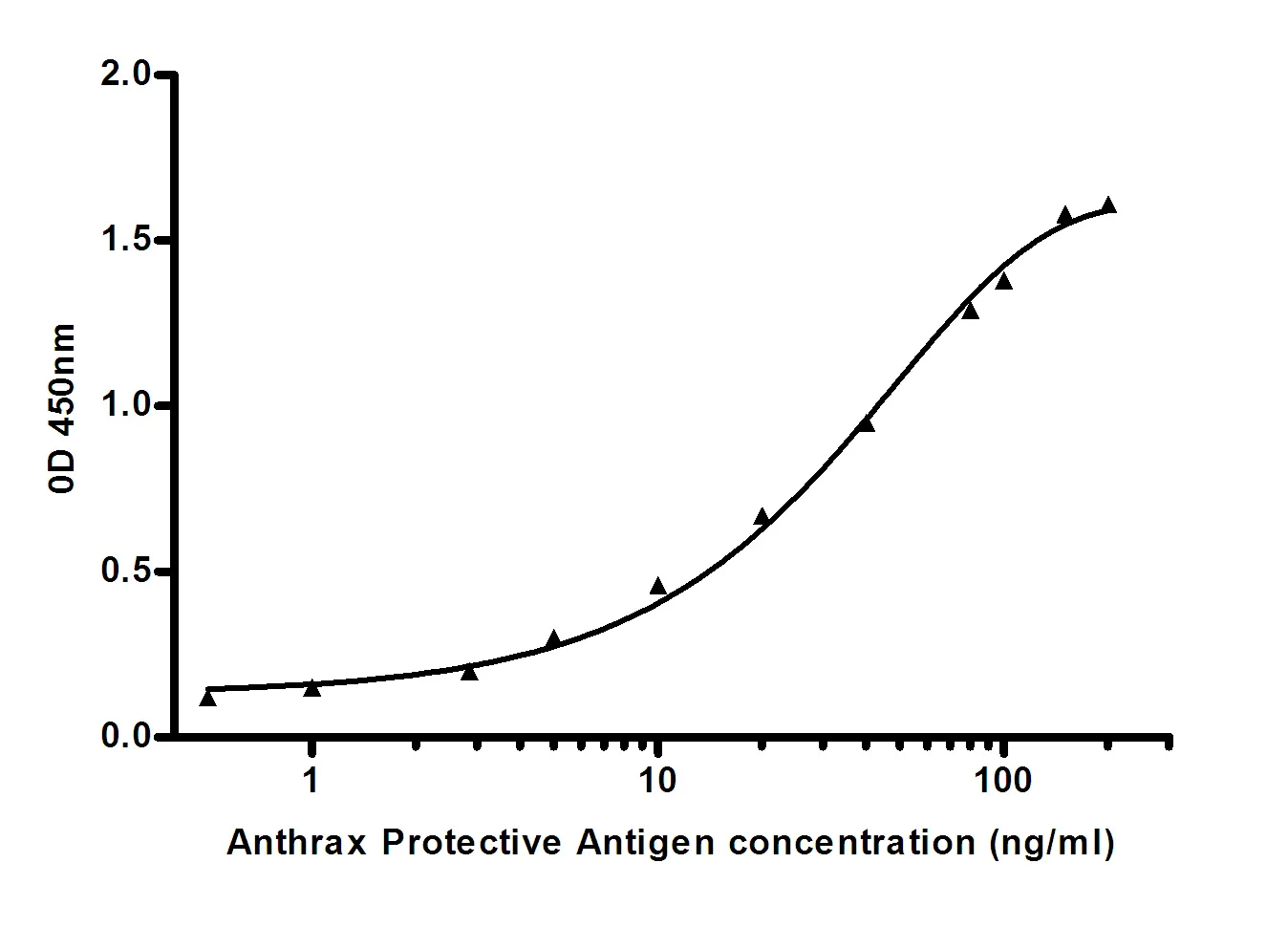
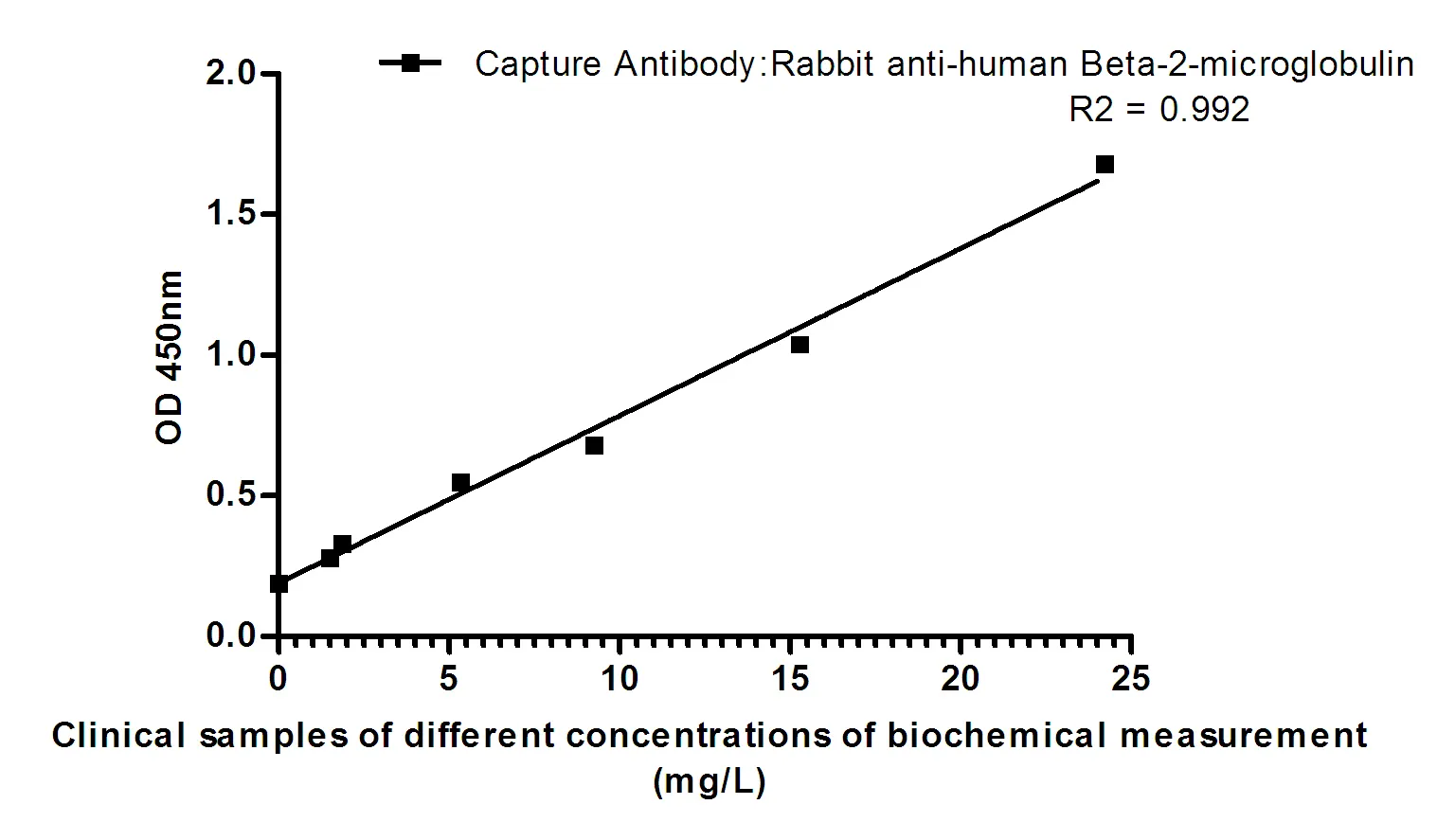
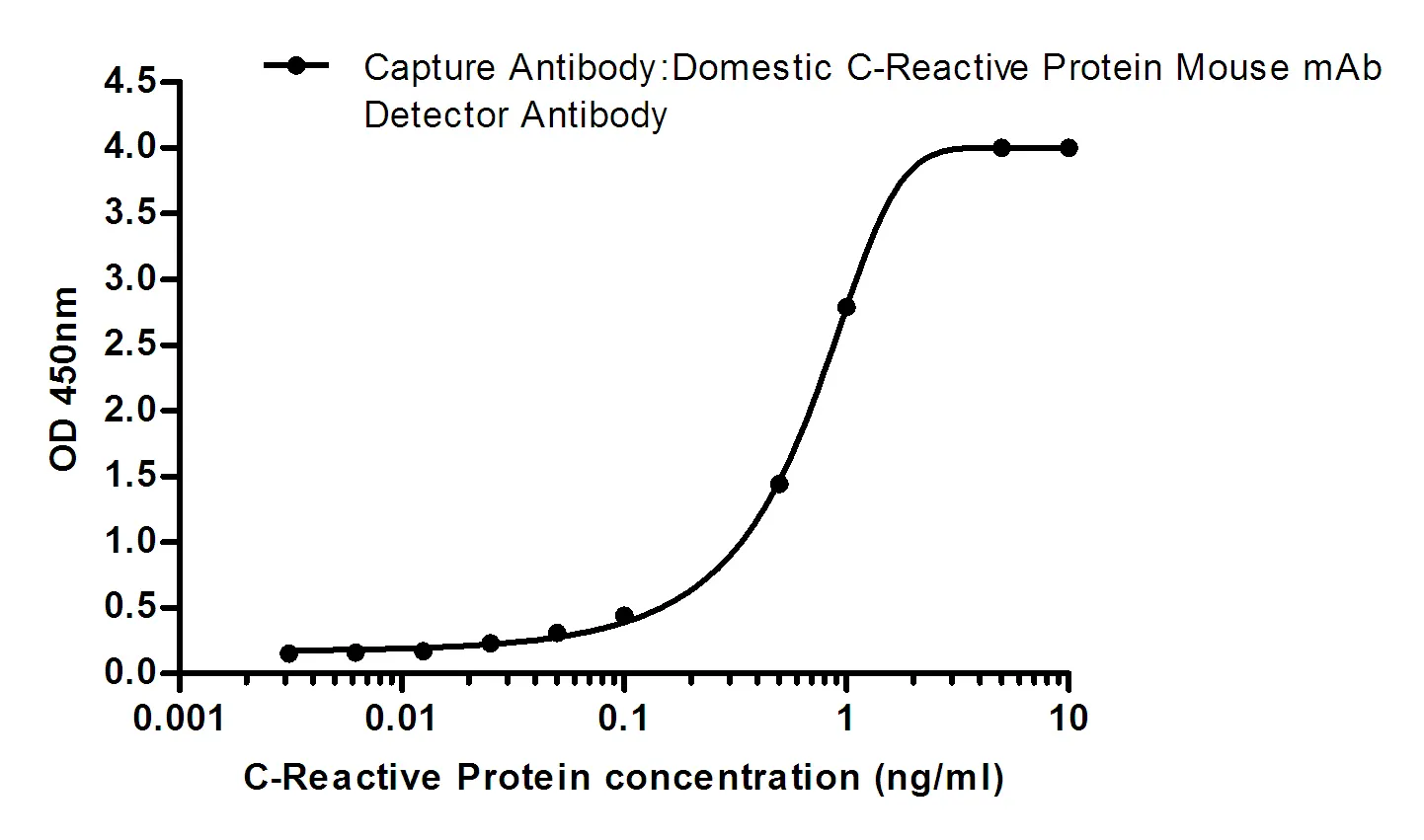
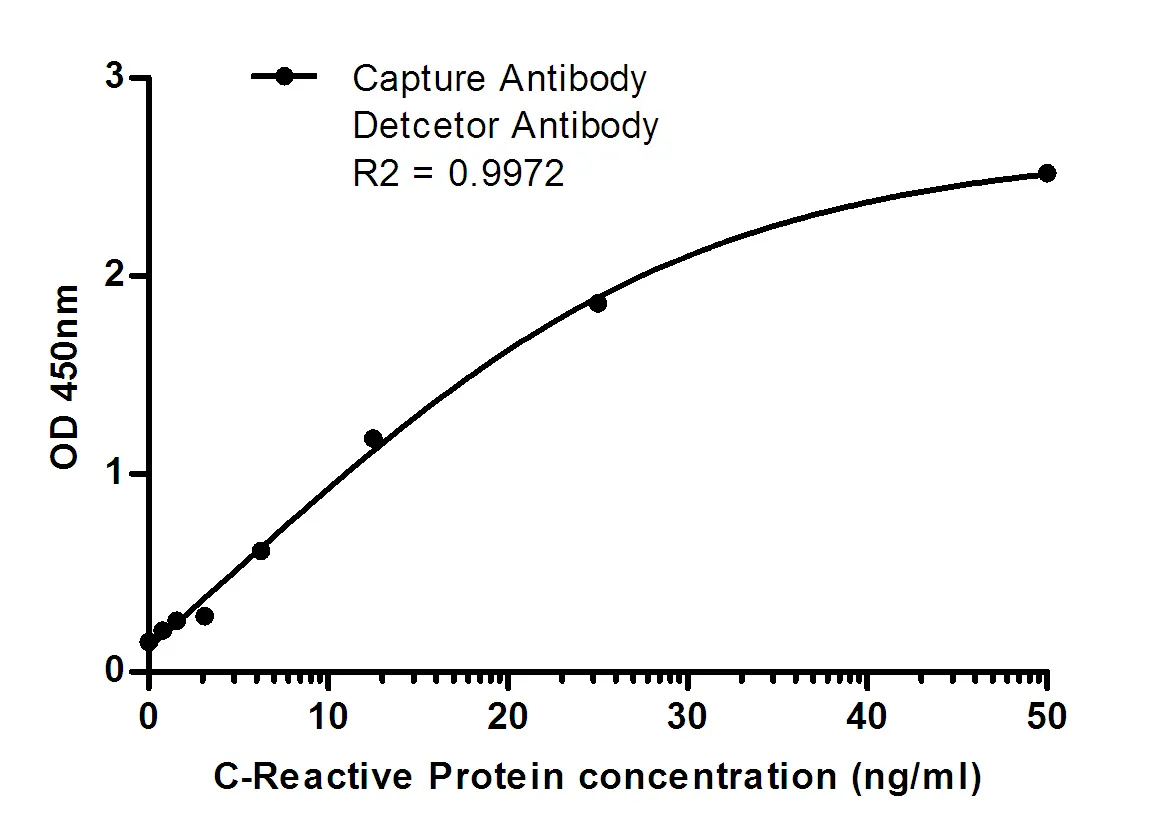
Summary
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
Members of the Smad family of signal transduction molecules are components of a critical intracellular pathway that transmit TGF-β signals from the cell surface into the nucleus. Three distinct classes of Smads have been defined: the receptor-regulated Smads (R-Smads), which include Smad1, 2, 3, 5, and 8; the common-mediator Smad (co-Smad), Smad4; and the antagonistic or inhibitory Smads (I-Smads), Smad6 and 7 . Activated type I receptors associate with specific R-Smads and phosphorylate them on a conserved carboxy terminal SSXS motif. The phosphorylated R-Smad dissociates from the receptor and forms a heteromeric complex with the co-Smad (Smad4), allowing translocation of the complex to the nucleus. Once in the nucleus, Smads can target a variety of DNA binding proteins to regulate transcriptional responses .
Research Area
Signal Transduction