Mide adenokarsinomu, mide kanserindeki en yaygın patoloji tipidir (tüm mide kanserlerinin yaklaşık %90'ı). Mide adenokarsinunun oluşumu normal mide mukozası ile başlar ve "kronik inflamasyon → atrofik gastrit → intestinal metaplazi → displazi (intraepitelyal neoplazi)" kademeli gelişim sürecini geçirir, her aşama moleküler seviyede anormal birikim ile eşlik eder. Temel mekanizma üç ana bağlantıya ayrılabilir: dış tetikleyici, kronik inflamatuvar drive ve moleküler genetik anormallikler [1, 2].
Dış çevresel faktörler mide adenokarsinunun temel nedenleridir, bunlar arasında Helicobacter pylori (Hp) enfeksiyonu WHO tarafından tanımlanan en kesin sınıf I kanserojen faktörüdür ve diğer faktörler sinerjistik veya üst üste binen etkiler yoluyla hasarı artırır, örneğin yüksek tuzlu diyetin uzun süreli alımı ve genetik yatkınlık [3].
Mukozal bariyer tahribati ve epitel atrofisi: inflamatuvar faktörler (örneğin IL-1β, TNF-α) mide mukozal epitel hücrelerinin çoğalmasını ve farklılaşmasını engelleyerek fonstik bez atrofisine (mide asit sekresyonunda azalma) yol açar ve mukozanın zarar verici faktörlere karşı direncini daha da azaltır;
Bağırsak metaplazisi (IM): mide asit azalmasının ortamına uyum sağlamak için, mide mukozal epitelyumu bağırsak epitelyumu ile değiştirilir (goblet hücrelerinin ve absorbsiyon hücrelerinin görünümü gibi) ve bu süreç gen ifadesi paternlerindeki değişikliklerle eşlik eder (CDX2 ve MUC2 gibi bağırsak epitelyum belirteçlerinin ifadesinin yükseltilmesi gibi), ve bağırsak metaplazya epitelyumu daha yüksek proliferatif aktiviteye sahiptir ve mutasyon birikimine daha yatkındır.
Displazi (intraepitelyal neoplazi): Bağırsak metaplazisi daha da gelişir, epitelyal hücreler morfolojik ve yapısal anormalliklere sahiptir (büyük çekirdekler, belirgin nükleoller ve düzensiz düzenleme gibi), ve hücre proliferasyonu kontrol dışıdır (Ki-67 indeksinin yükselmesi gibi), ancak henüz bazal membranı geçmemiştir ("prekanseröz lezyonlara" aittir), bu aşama kanseri geri çevirmede kilit bir düğümdür, ve eğer müdahale edilmezse, orta ila şiddetli displazinin yaklaşık %5'-%10'u 5 yıl içinde adenokarsinomaya ilerler [4].
With the accumulation of mucosal damage, gastric mucosal cells gradually develop genetic mutations, chromosomal abnormalities, and epigenetic changes, ultimately leading to malignant phenotypes such as "unlimited proliferation, anti-apoptosis, and invasive metastasis".
RAS-MAPK pathway activation: Approximately 10%-20% of gastric adenocarcinomas have KRAS or NRAS gene mutations, leading to continuous activation of the pathway, promoting cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis.
PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway activation: Approximately 30%-40% of gastric adenocarcinomas have PIK3CA gene mutations (encoding PI3K catalytic subunits) or PTEN gene inactivation (negatively regulating the PI3K pathway), which can promote cell metabolism, angiogenesis and invasion after pathway activation.
TP53 gene mutation: One of the most common mutations in gastric adenocarcinoma (incidence of about 50%-60%), TP53 is the "genome guardian" that loses the function of DNA damage repair and induce apoptosis after mutation, allowing abnormal cells to survive and accumulate more mutations;
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection: Approximately 10% of gastric adenocarcinomas are associated with EBV infection (EBV-associated gastric cancer), which activates pathways such as NF-κB and PI3K by encoding proteins such as latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1), promoting inflammation and cell proliferation, while EBV infection can lead to abnormal DNA methylation (such as silencing tumor suppressor genes) [5].
DNA methylation: For example, the hypermethylation of the promoter region of tumor suppressor genes p16INK4a and MLH1 leads to gene silencing (unable to express proteins) and losing cell cycle regulation and DNA repair functions, respectively.
Histone modifications: such as histone deacetylate (HDAC) leads to chromatin concentration, and transcription of tumor suppressor genes is inhibited.
CAFs secrete ECM components such as collagen and fibronectin, forming a physical barrier that prevents immune cell infiltration. At the same time, it secretes cytokines such as IL-6 and TGF-β to promote the proliferation and invasion of tumor cells.
Immunosuppressive cells (such as Tregs) secrete IL-10, TGF-β, which inhibit effector T cell function, leading to "immune escape" and allowing tumor cells to grow.
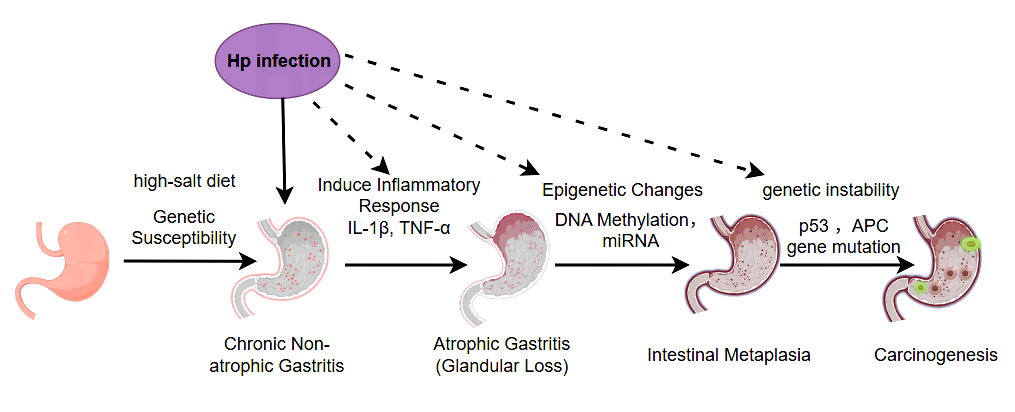
Diyagram: Mide Adenokarsinomu Patogenezi (Hp enfeksiyonu, yüksek tuzlu diyet, inflamatuvar yanıt, genetik & epigenetik değişiklikler)
| Hedef | Katalog# | Ürün Adı | Reaktivite | Uygulama |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HP yolu ile ilgili antikorlar | ||||
| COX-2 | AMRe09271 | COX2 (15D12) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF, IP, IF-P |
| COX-2 | AMRe01845 | Cyclooxygenase 2 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P |
| Antibodies related to the uncontrolled pathway of gastric mucosal cell proliferation | ||||
| Cyclin D1 | AMRe09589 | Cyclin D1 (10Z18) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF, IP, IF-P |
| p16INK4a | AMRe15577 | p16 INK (16J3) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB, IHC-P, FC, IP, IF-P |
| p16INK4a | AMRe01811 | CDKN2A/p16INK4a Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, ICC/IF |
| CDKN1A | AMRe02380 | p21 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB |
| RB1 | AMRe03902 | Phospho-Rb (Ser807) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-F, IHC-P, ICC/IF |
| RB1 | AMRe05995 | Phospho-Retinoblastoma (S807) (4H3) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF, IF-P |
| c-Myc | AMRe05879 | Phospho-c-Myc (S62) (9Z2) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF, FC, IP, IF-P |
| c-Myc | AMRe05880 | Phospho-c-Myc (T58) (1A2) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ICC/IF, FC |
| HER2 | AMRe10568 | ErbB2 (HER2) (4J7) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF, FC, IP, IF-P |
| MET | AMRe02248 | c-Met Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-F, IHC-P, ICC/IF |
| CDK4 | AMRe01808 | CDK4 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-F, IHC-P, ICC/IF, IP |
| CDK6 | APRab08569 | Cdk6 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | - | WB, IHC-P, IF-P, IF-F, ICC/IF, ELISA |
| Antibodies related to tumor microenvironment and angiogenesis pathway | ||||
| P53 | AMRe03901 | Phospho-p53 (Ser392) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-F, IHC-P, IP |
| P53 | AMRe02388 | p53 Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | Mouse | WB,ICC/IF,IP |
| Bcl-2 | AMRe03755 | Bcl2 Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | Human, Mouse | WB,IHC-P |
| Bax | AMRe03742 | Bax Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, IP |
| Caspase-3 | AMRe01762 | Cleaved-Caspase 3 p12 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ICC/IF |
| Caspase-3 | AMRe01567 | Caspase 3 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, IP |
| Caspase-9 | AMRe04045 | Caspase 9 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, IP |
| SMAD2 | AMRe03795 | Smad2 Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | Human,Rat,Hamster | WB,IHC-F,IHC-P,ICC/IF,IP |
| SMAD4 | AMRe03205 | Smad4 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Rat | WB, ICC/IF, IP |
| ZEB1 | AMRe20076 | ZEB1 (16B4) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF, FC, IF-P |
| AKT1 | AMRe06740 | AKT1 (5O1) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF, FC, IP, IF-P |
| PTEN | AMRe16636 | PTEN (16Q18) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, FC, IP, IF-P |
| mTOR | AMRe02286 | Phospho-mTOR (Ser2448) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, IHC-P |
| KRAS | APRab13128 | K-Ras Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, IF-P, IF-F, ICC/IF, ELISA |
| NRAS | AMRe02525 | GTPase HRAS Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ICC/IF, IP |
| ERK1 | AMRe03741 | ERK1/2 Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB,ICC/IF,IP |
| VEGFA | AMRe02757 | VEGFA Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB |
| FGFR2 | AMRe10945 | FGFR2 (18K11) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IP |
| CA9 | AMRe07799 | CA9 (14N17) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, IP, IF-P |
| CLDN1 | AMRe08890 | Claudin 1 (5F6) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF, FC, IP, IF-P |
| Antibodies associated with inflammatory and immune regulatory pathways | ||||
| TNFα | AMM19084 | TNF α(Q34) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, IF-P, IF-F, ICC/IF |
| IL-6 | APRab03851 | IL-6 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human | WB, IHC-P, ELISA |
| IL-8 | AMRe12568 | IL8 (6Z6) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB |
| IL-10 | AMRe12483 | IL10 (8U9) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB, ICC/IF, FC |
| TGF-β1 | AMM00661 | TGF beta 1 (8F6) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P |
| STAT3 | AMRe06021 | Phospho-STAT3 (Y705) (13H8) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF, FC, IP, IF-P |
| STAT3 | AMRe18352 | STAT3 (11W6) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF, FC, IF-P |
| Galectin-9 | APRab11278 | Galectin-9 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, IF-P, IF-F, ICC/IF, ELISA |
| NLRP3 | AMRe01571 | NLRP3 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB |
| NLRP3 | AMRe14399 | NALP3 (8Q17) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, FC, IP |
| PD-L1 | AMRe15922 | PD-L1 (CD274) (5R18) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF, FC, IP, IF-P |
| PD-1 | AMRe15873 | PD L2 (12P7) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB |
| CTLA-4 | AMRe09507 | CTLA4 (CD152) (14H2) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, IHC-P, FC, IP, IF-P |
| Other relevant antibodies | ||||
| Vimentin | AMRe03745 | Vimentin Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat, Hamster | WB, IHC-F, IHC-P, ICC/IF |
| CD44 | AMRe08400 | CD44 (19J7) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, IP, IF-P |
| E-Cadherin | AMRe01411 | E Cadherin Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB,IHC-F,IHC-P,ICC/IF,IP |
| MMP3 | AMRe02266 | MMP3 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P |
| MMP7 | APRab13996 | MMP-7 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey | WB, IHC-P, IF-P, IF-F, ICC/IF, ELISA |
| MMP9 | AMRe02267 | MMP9 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Rat | WB, IHC-P, IP |
| MMP9 | APRab14000 | MMP-9 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC-P, IF-P, IF-F, ICC/IF, ELISA |
| MMP13 | APRab13979 | MMP-13 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human, Rat, Mouse | WB, IHC-P, IF-P, IF-F, ICC/IF, ELISA |
| CA125 | APRab14240 | Mucin 16 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human, Rat, Mouse | WB, IHC-P |
| Hedef | Katalog# | Ürün Adı | Reaktivite | Tespit Aralığı | Hassasiyet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEGFA | EM10657 | Mouse VEGF-A (Vascular Endothelial Cell Growth Factor A) ELISA Kit | Mouse | 31.25-2000pg/mL | 18.75pg/mL |
| MMP3 | EH10202 | Human MMP-3 (Matrix Metalloproteinase 3) ELISA Kit | Human | 0.16-10ng/mL | 0.1ng/mL |
| MMP9 | EM10682 | Mouse Pro-MMP-9 (Pro-Matrix Metalloproteinase-9) ELISA Kit | Mouse | 78.13-5000pg/mL | 46.88pg/mL |
| MMP9 | EH10079 | Human MMP-9 (Matrix Metalloproteinase 9) ELISA Kit | Human | 0.16-10ng/mL | 0.1ng/mL |
| CA125 | EH10414 | Human CA125 (Carbohydrate Antigen 125) ELISA Kit | Human | 3.13-200IU/mL | 1.88IU/mL |
| TNFα | EH10021 | Human TNF-α (Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit | Human | 7.81-500pg/mL | 4.69pg/mL |
| TNFα | EM27661S | High Sensitivity Mouse TNF-α (Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit | Mouse | 1.56-100pg/mL | 0.93pg/mL |
| IL-1β | EM27654S | Mouse IL-1β (Interleukin 1 Beta) ELISA Kit | Mouse | 3.13-200pg/mL | 1.87pg/mL |
| IL-6 | EM21023S | High Sensitivity Mouse IL-6 (Interleukin 6) ELISA Kit | Mouse | 0.781-50pg/mL | 0.47pg/mL |
| IL-6 | EH10020 | Human IL-6 (Interleukin 6) ELISA Kit | Human | 1.56-100pg/mL | 0.94pg/mL |
İlgili Ürünler
Wang R, Song S, Harada K, et al. Mide adenokarsinomu nedenleri ile ilgili çoklu profillemesi, tedavi yanıtını öngören yeni hedefler ve moleküler alt tipleri tanımladı. Gut. 2020 Jan;69(1):18-31. Epub 2019 Jun 6. [PMID: 31171626].
Song S, Fan Y, Zou G, Huo L,et al. KAP1, HNRNPAB'a bağlanarak Hippo/YAP1 sinyalizasyonunu aktive ederek mide adenokarsinom progresyonunu teşvik eder. Cancer Lett. 2025 Jul 1;621:217695. Epub 2025 Apr 4. [PMID: 40189014].
Ng D, Cyr D, Khan S, Dossa F, Swallow C, Kazazian K. Mide adenokarsinomunda peritoneal disseminasyon metastazının moleküler mekanizmaları. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025 May 3;44(2):50. [PMID: 40317360].
Wiklund AK, Santoni G, Yan J, Radkiewicz C, et al. Helicobacter pylori eradicate edildikten sonra mide adenokarsinomu riski. Gastroenterology. 2025 Aug;169(2):244-250.e1. Epub 2025 Feb 7. [PMID: 39924057].
Song D, Liu Q, Yan Z, Wang Q, et al. WSGC@MS tarafından mide adenokarsinom proliferasyonunun inhibisyonu: KEAP1/NRF2 sinyal yolu ve otorequlasyonunun rolü. Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jun 16;33:101995.[ PMID: 40688680].
 | Flora, immünoloji ve nörobilim konularına hakim bir EnkiLife teknik destek uzmanıdır. Müşterilere nörodejeneratif hastalıklar ve diğer nörobilim alanlarında araştırma yapmalarına yardımcı olmak için yüksek kaliteli ürün kombinasyonları ve teknik destek sağlamaya kendini adamıştır. |
© 2025 EnkiLife Mide adenokarsinomu Araştırma Materyalleri | Profesyonel Antikorlar ve ELISA Kitleri Sağlama
